Introduction
How does a cart change its motion when you push and pull on it? You might think that the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or, is the force related to something else? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one.
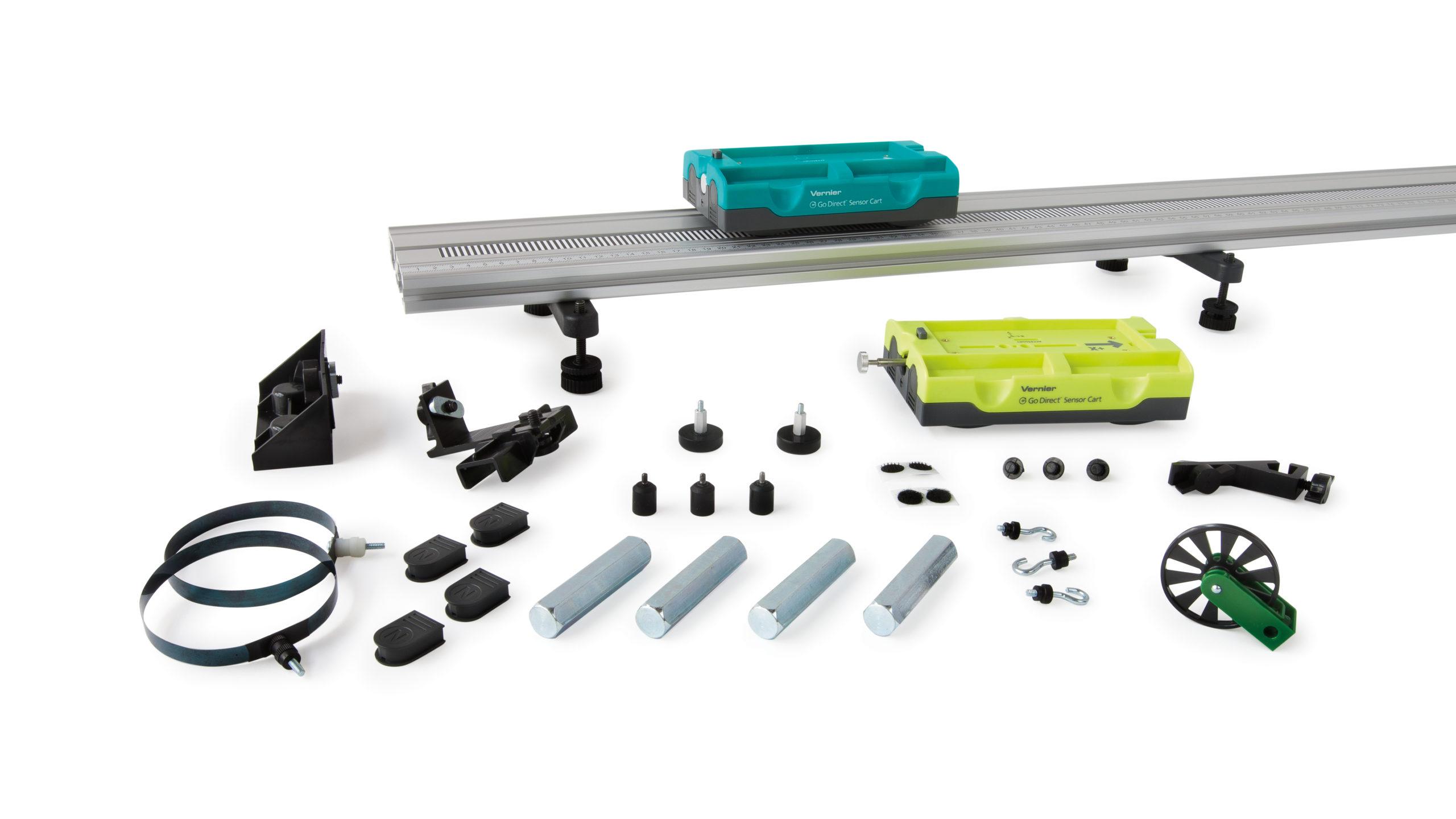
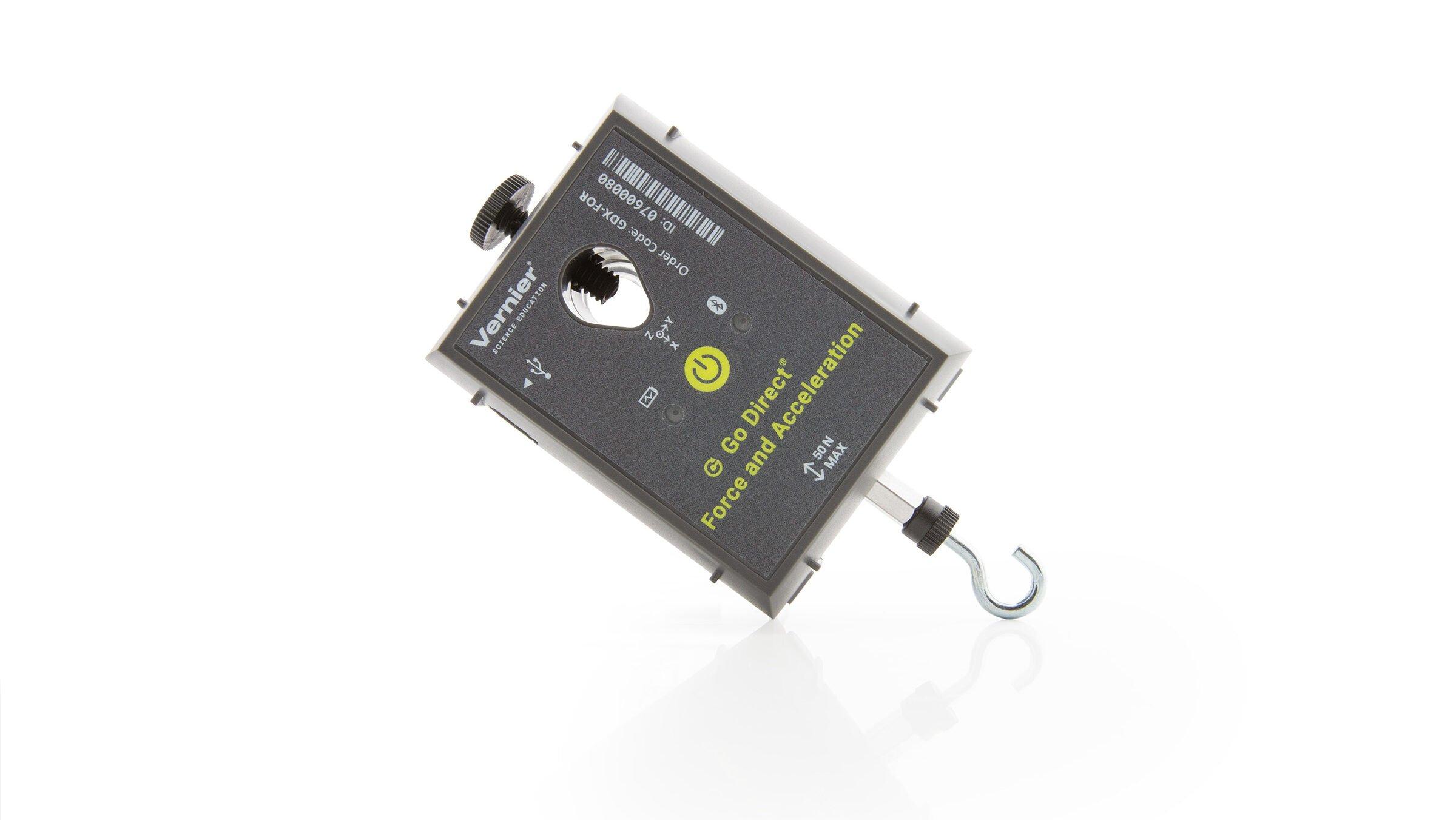
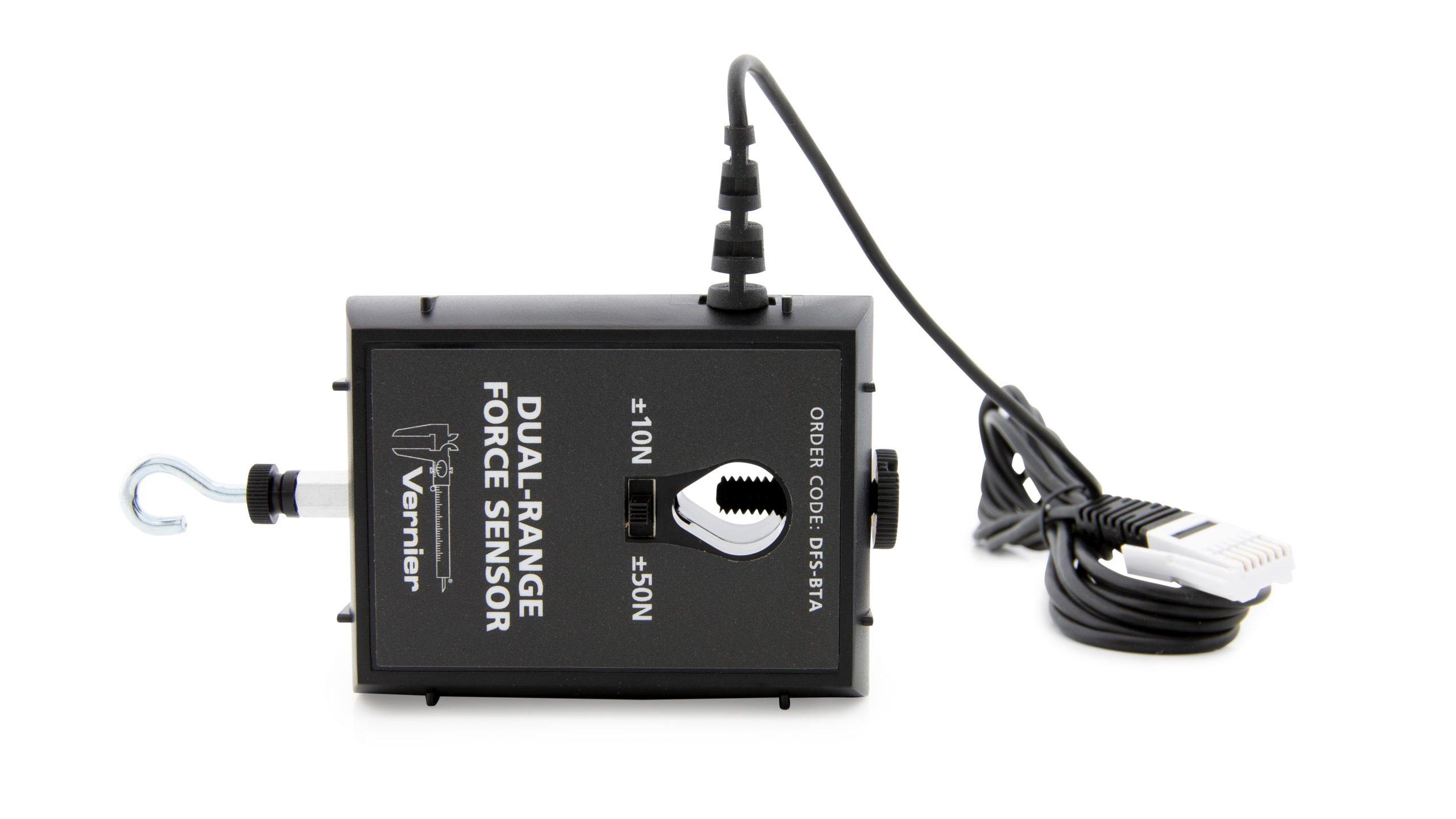
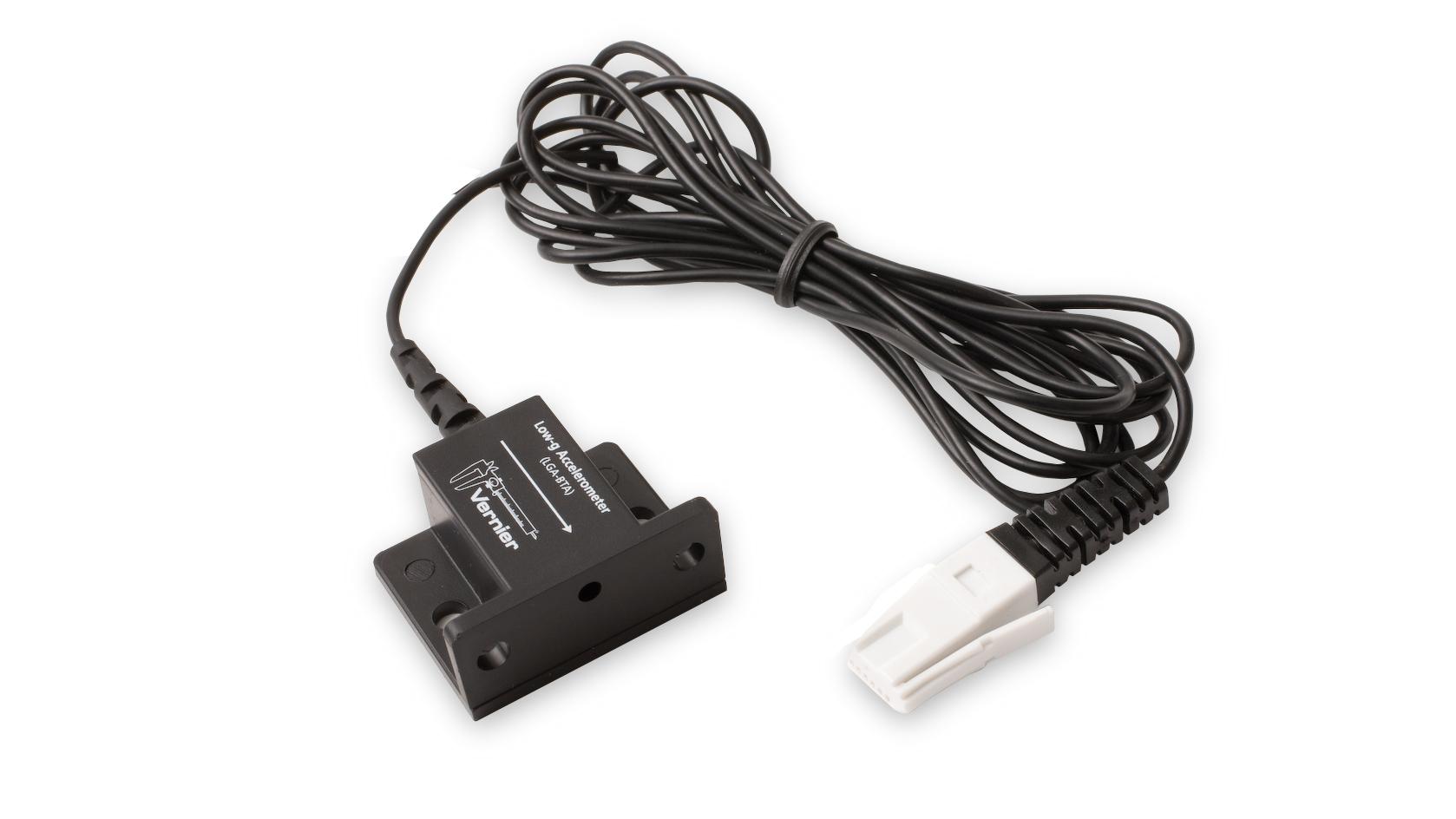
A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with the cart’s acceleration. The total mass of the cart is easy to vary by adding masses. Using these tools, you can determine how the net force on the cart, its mass, and its acceleration are related. This relationship is Newton’s second law of motion.
Objectives
- Collect force and acceleration data for a cart as it is moved back and forth.
- Compare force vs. time and acceleration vs. time graphs.
- Analyze a graph of force vs. acceleration.
- Determine the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #9 of Physics with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.






