Introduction
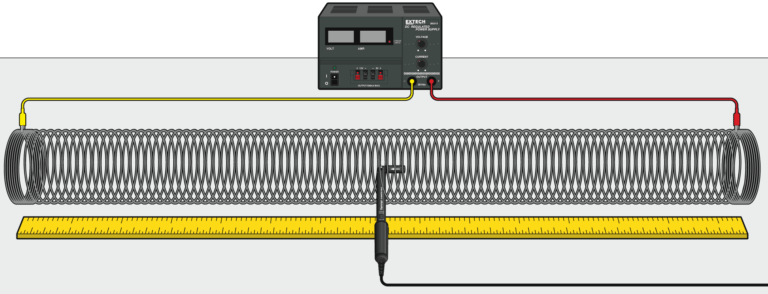
A solenoid is made by taking a tube and wrapping it with many turns of wire. A metal Slinky® is the same shape and will serve as a solenoid. When a current passes through the wire, a magnetic field is present inside the solenoid. Solenoids are used in electronic circuits or as electromagnets.
In this lab you will explore factors that affect the magnetic field inside the solenoid and study how the field varies in different parts of the solenoid. By inserting a Magnetic Field Sensor between the coils of the Slinky, you can measure the magnetic field inside the coil. You will also measure µ0, the permeability constant. The permeability constant is a fundamental constant of physics.
Objectives
- Determine the relationship between magnetic field and the current in a solenoid.
- Determine the relationship between magnetic field and the number of turns per meter in a solenoid.
- Study how the field varies inside and outside a solenoid.
- Determine the value of µ0, the permeability constant.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #26 of Physics with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.





