Introduction
You may have learned this statement of Newton’s third law: “To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” What does this sentence mean? This experiment will help you investigate this question.
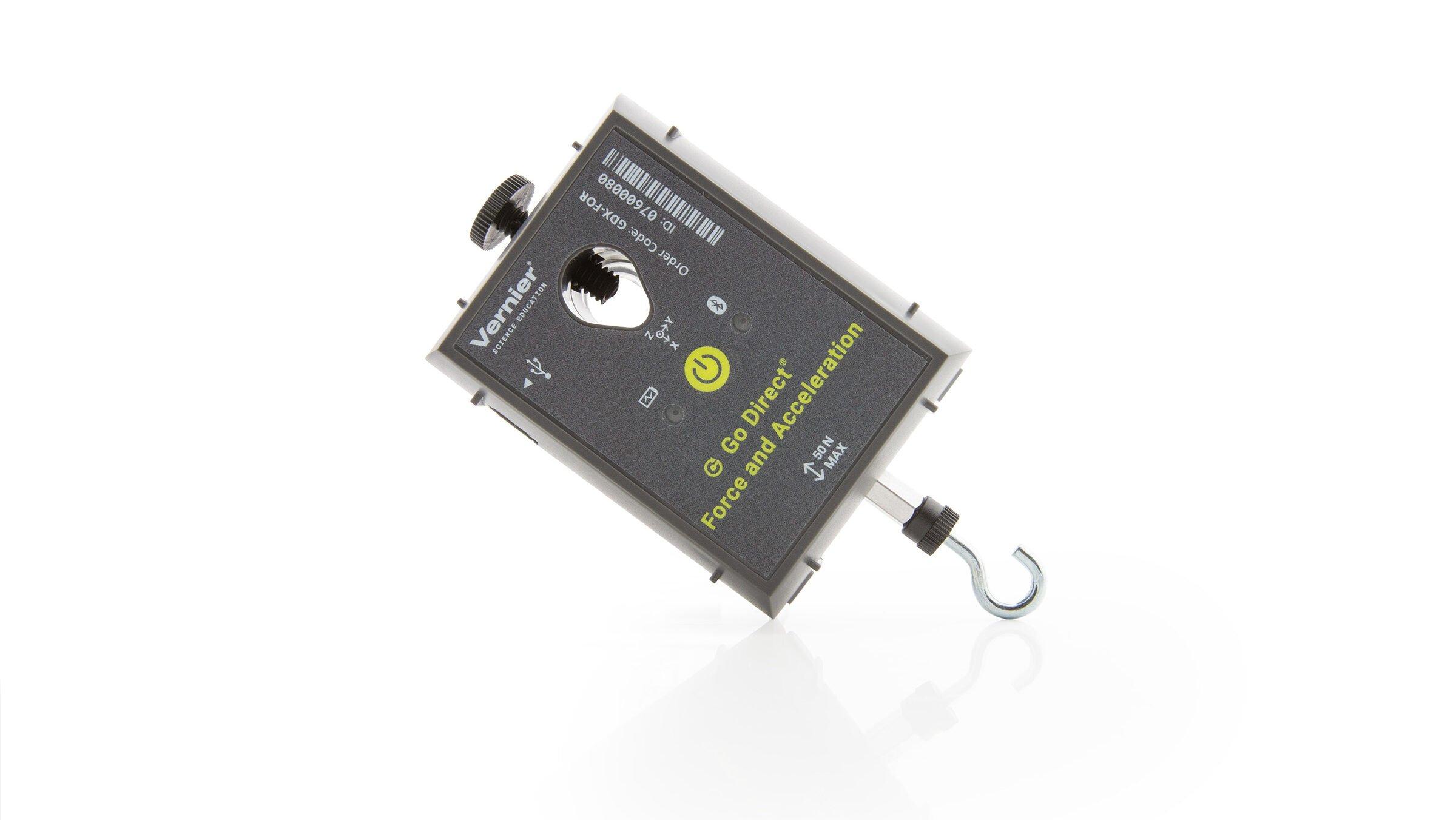
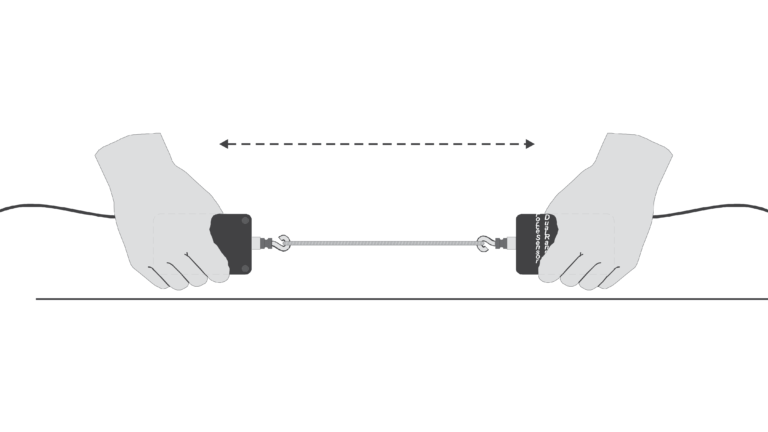
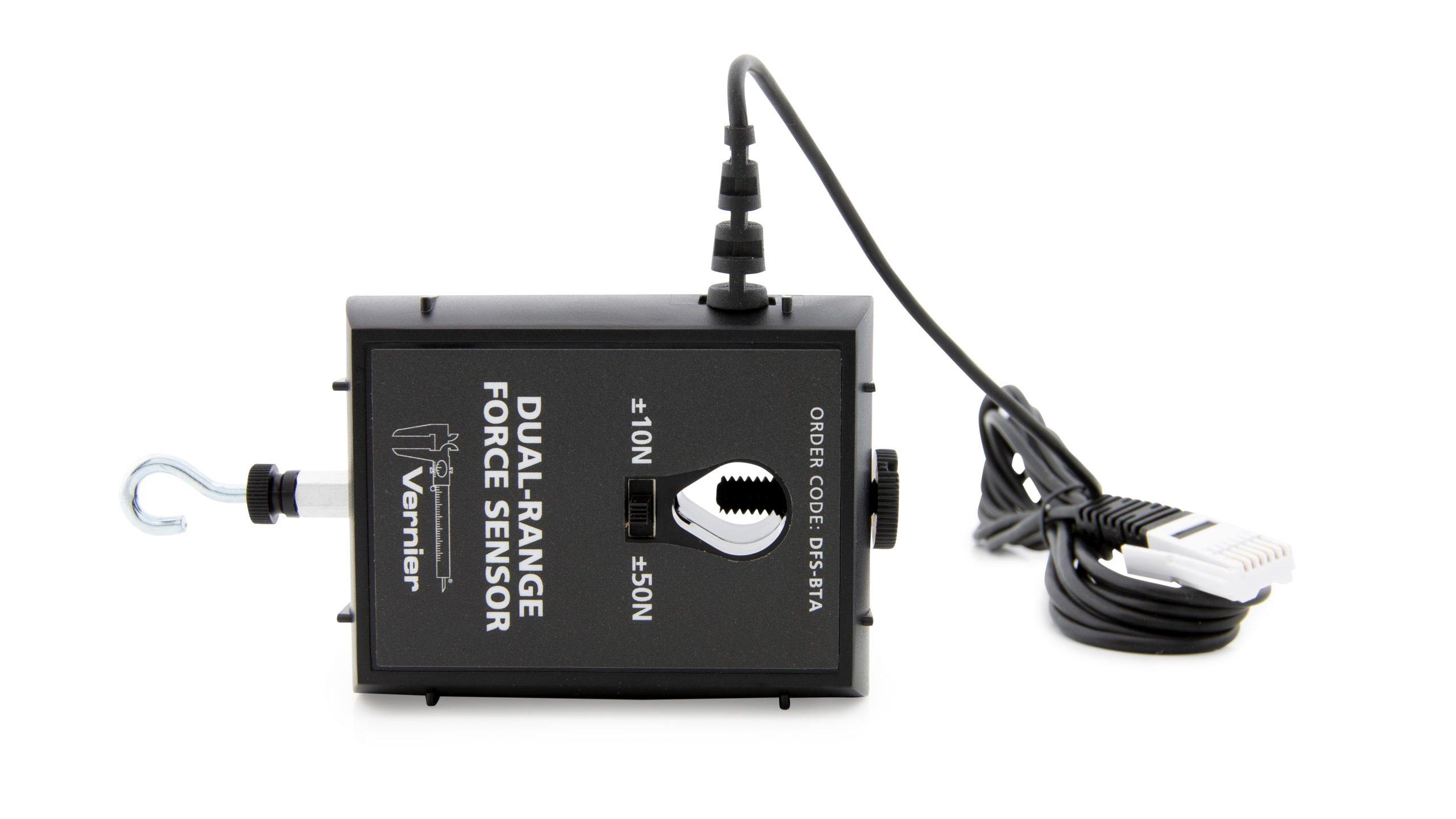
Unlike Newton’s first two laws of motion, which concern only individual objects, the third law describes an interaction between two bodies. For example, what if you pull on your partner’s hand with your hand? To study this interaction, you can use two Force Sensors. As one object (your hand) pushes or pulls on another object (your partner’s hand), the Force Sensors will record those pushes and pulls. They will be related in a very simple way as predicted by Newton’s third law.
The action referred to in the phrase above is the force applied by your hand, and the reaction is the force that is applied by your partner’s hand. Together, they are known as a force pair. This short experiment will show how the forces are related.
Objectives
- Observe the directional relationship between force pairs.
- Observe the time variation of force pairs.
- Explain Newton’s third law in simple language.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 2

Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #11 of Physics with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.



