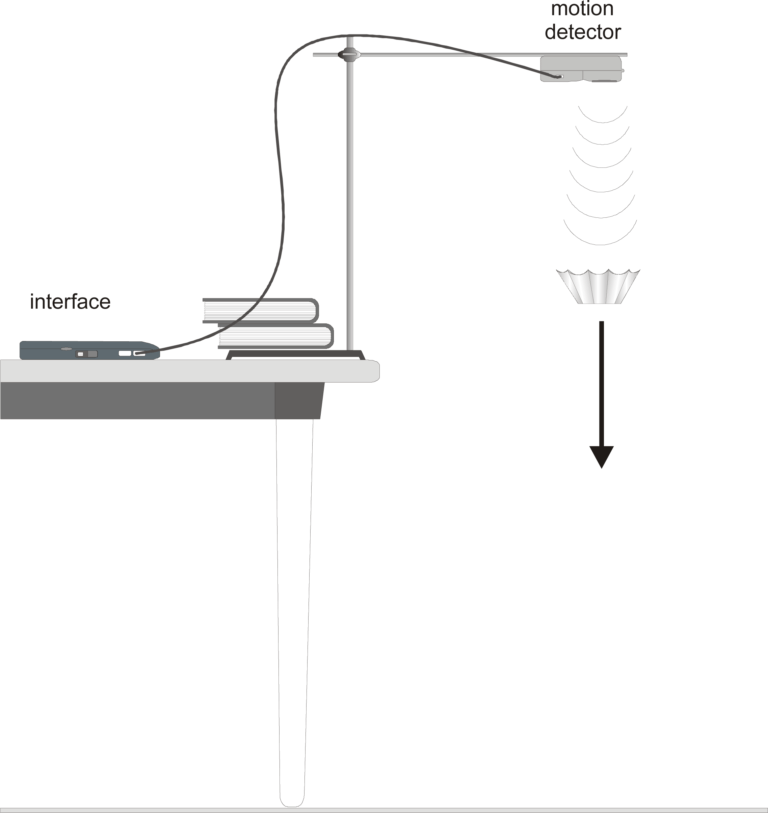
Introduction
Galileo tried to prove that all falling objects accelerate downward at the same rate. Falling objects do accelerate downward at the same rate in a vacuum. Air resistance, however, can cause objects to fall at different rates in air. Air resistance enables a skydiver’s parachute to slow his or her fall. Because of air resistance, falling objects can reach a maximum velocity or terminal velocity. In this experiment, you will study the velocities of two different falling objects.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Use a Motion Detector to measure position and velocity.
- Produce position vs. time and velocity vs. time graphs.
- Analyze and explain the results.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1

Option 2

Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #40 of Physical Science with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.

