Gas Temperature and Pressure
Experiment #31 from Physical Science with Vernier
- Subject
- Physical Science

Introduction
Gases are made up of tiny particles. The particles are in constant motion and exert pressure when they strike the walls of their container. In this simple experiment, you will use a computerinterfaced pressure sensor and an air sample in a stoppered flask to study the relationship between gas pressure and temperature. The volume and amount of gas will be kept constant. The results will be expressed in words, in a table, with a graph, and with a mathematical equation.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
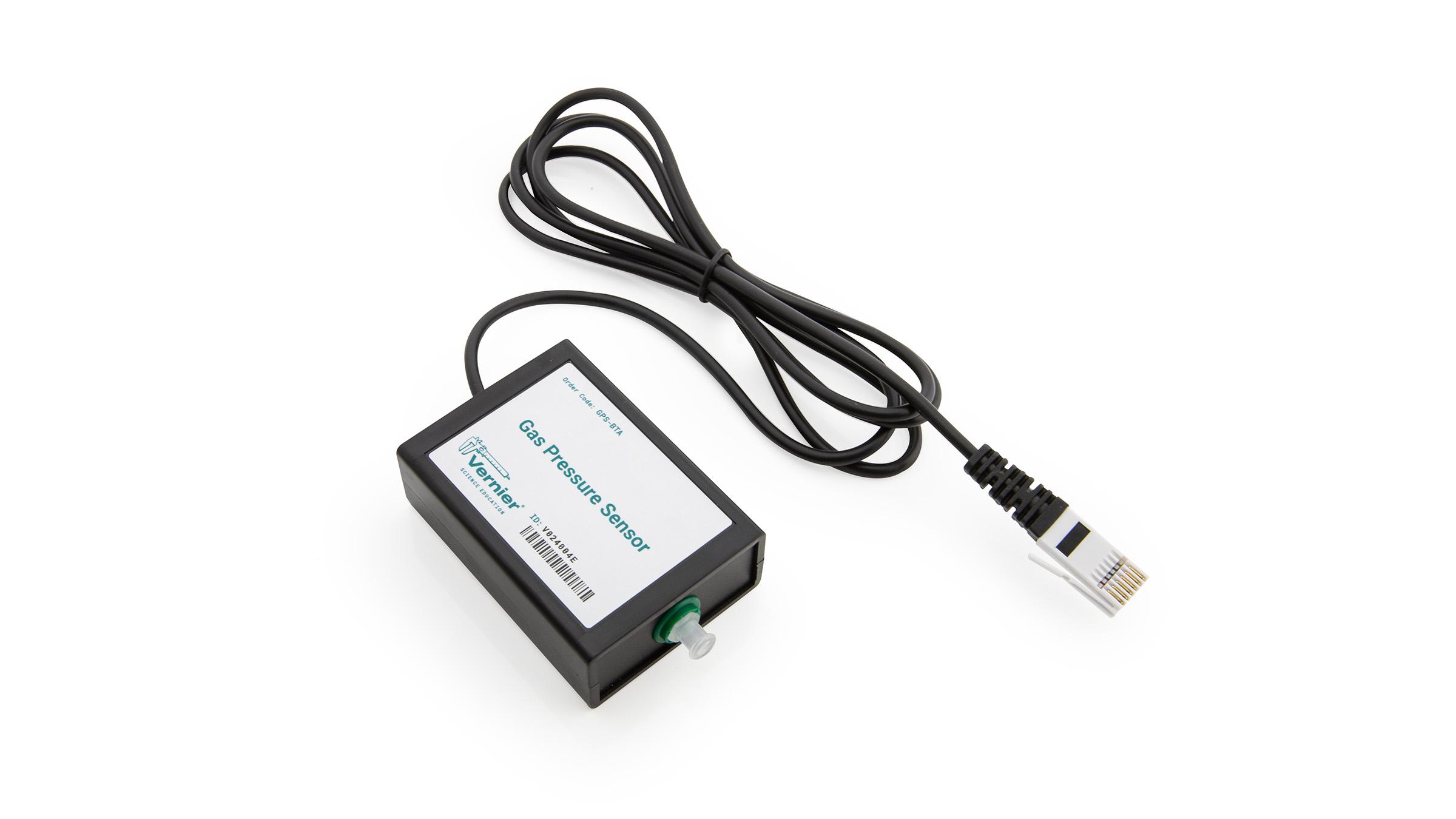
- Use a pressure sensor to measure the pressure of an air sample at several different temperatures.
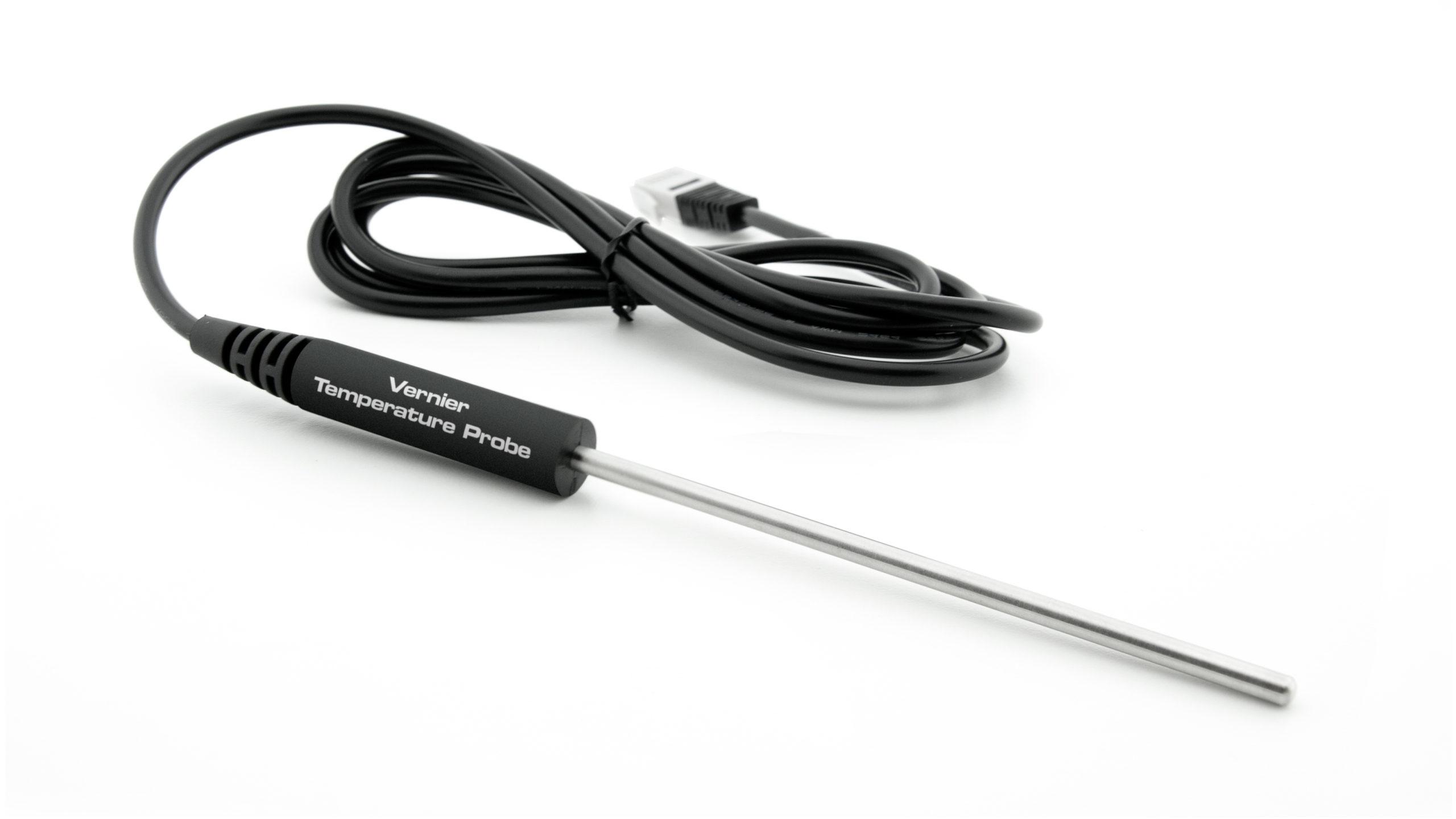
- Measure temperature.
- Make a table of the results.
- Graph the results.
- Predict the pressure at other temperatures.
- Describe the relationship between gas pressure and temperature with words and with a mathematical equation.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #31 of Physical Science with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.