Introduction
In this experiment, you will study the electrical conductivity of water and various water solutions. A solution can contain molecules, ions, or both. Some substances, such as sucrose (C12H22O11), dissolve to give a solution containing mostly molecules. An equation representing the dissolving of sucrose (table sugar) in water is
Other substances, such as calcium chloride (CaCl2), dissolve in water to produce a solution containing mostly ions. An equation is
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Write equations for the dissolving of substances in water.
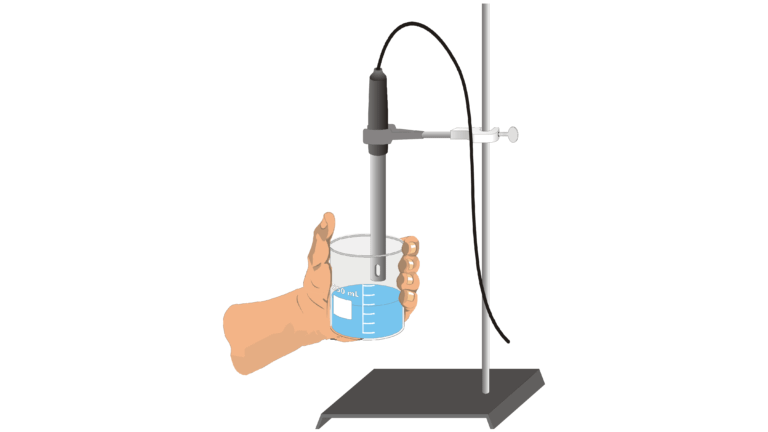
- Use a Conductivity Probe to test the electrical conductivity of solutions.
- Determine which, molecules or ions, are responsible for electrical conductivity of solutions.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1

Option 2

Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #16 of Physical Science with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.

