Investigating Centripetal Acceleration using a Centripetal Force Apparatus
Experiment #12 from Advanced Physics with Vernier — Mechanics
- Subject
- Physics
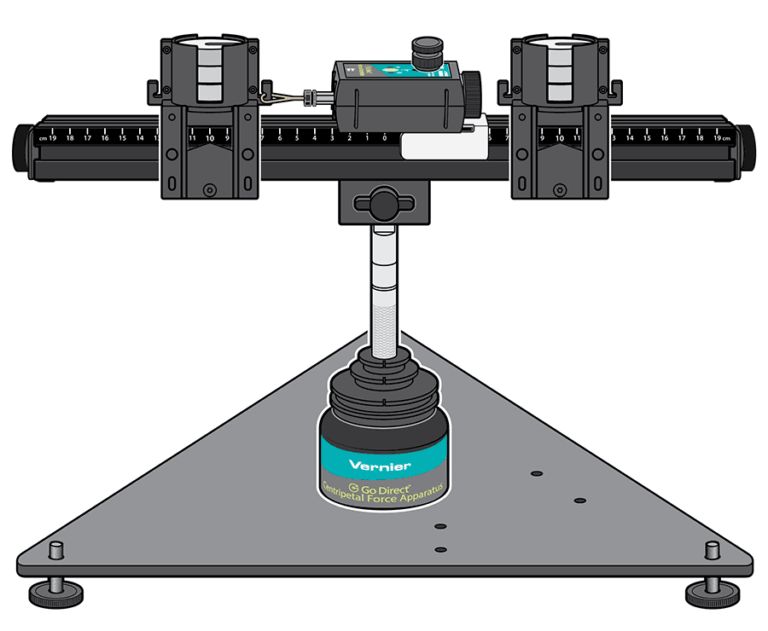
Introduction
The typical response when one hears the word acceleration is to think of an object changing its speed. You have also learned that velocity has both magnitude and direction. So, an object traveling at constant speed in a circular path is undergoing an acceleration. In this experiment you will develop an expression for this type of acceleration.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Analyze velocity vectors of an object undergoing uniform circular motion to determine the direction of the acceleration vector at any given moment.
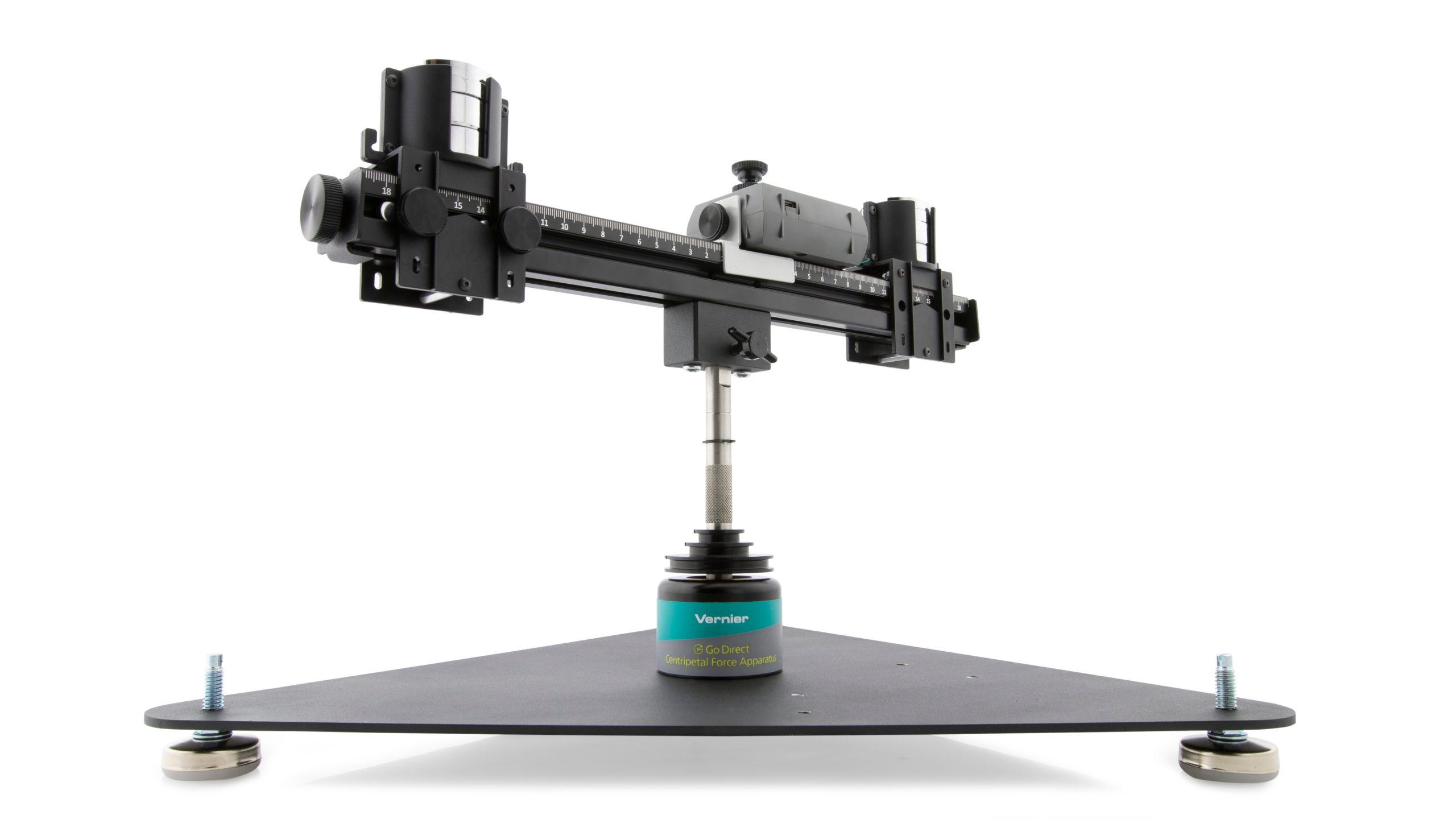
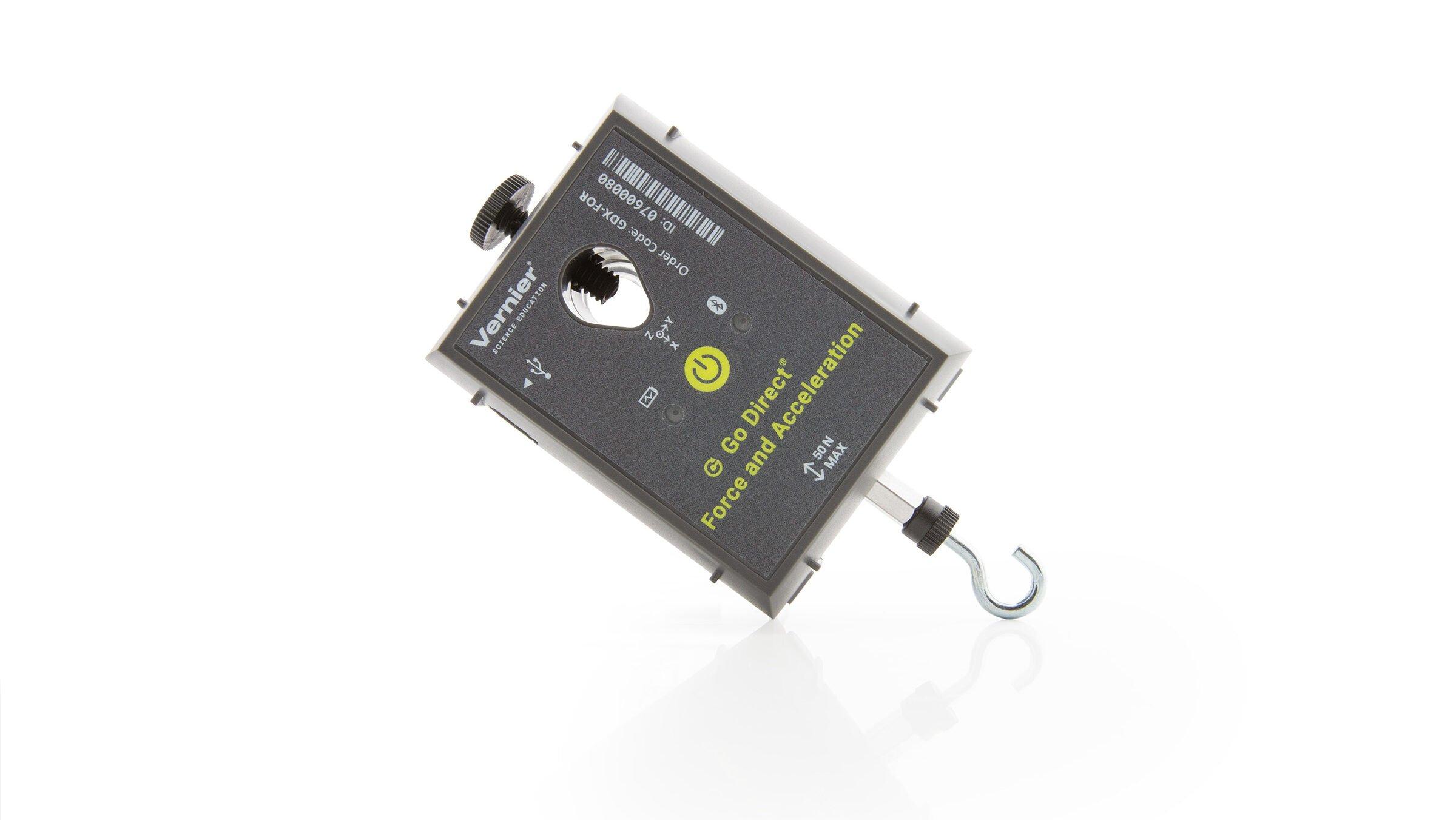
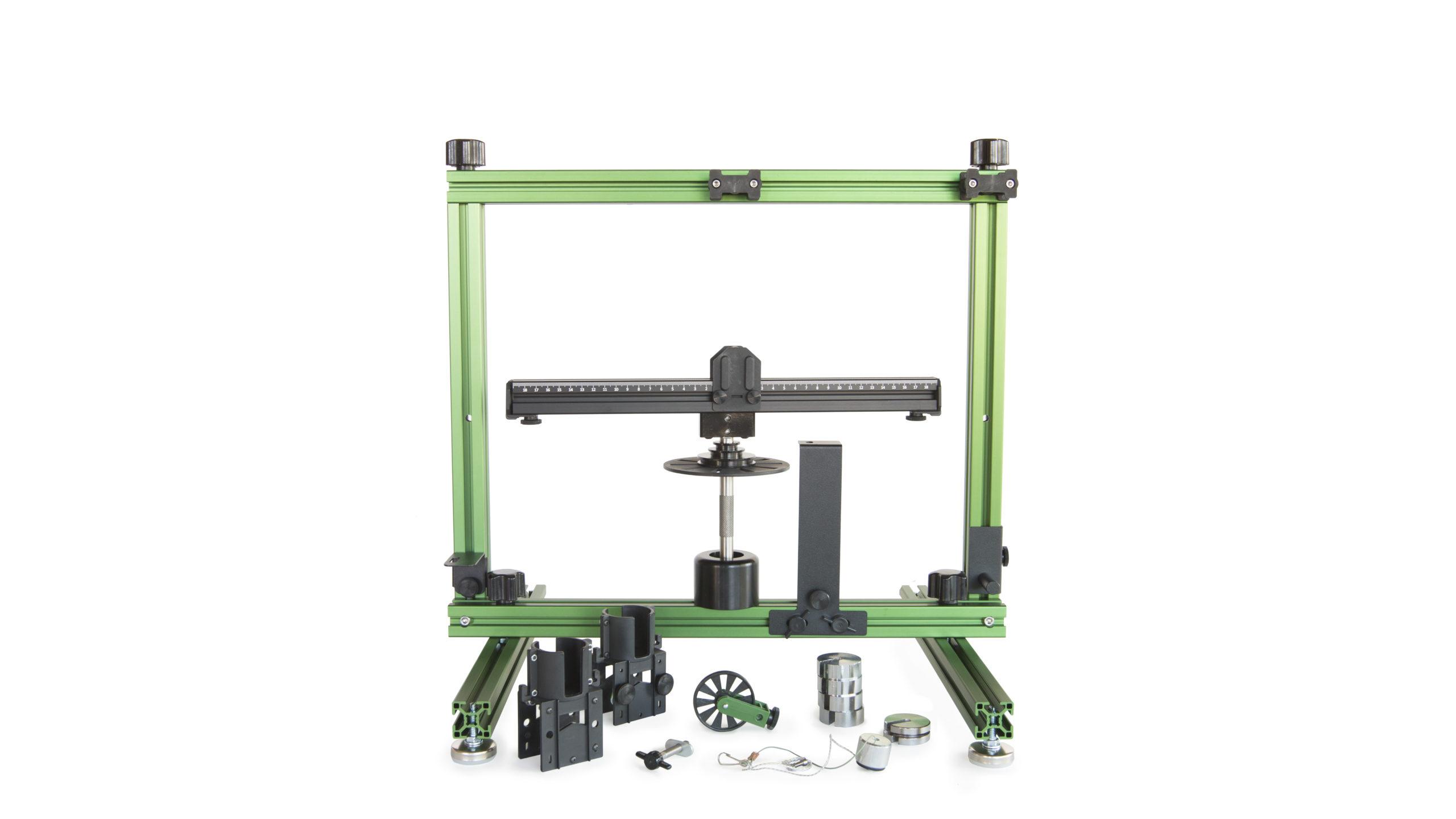
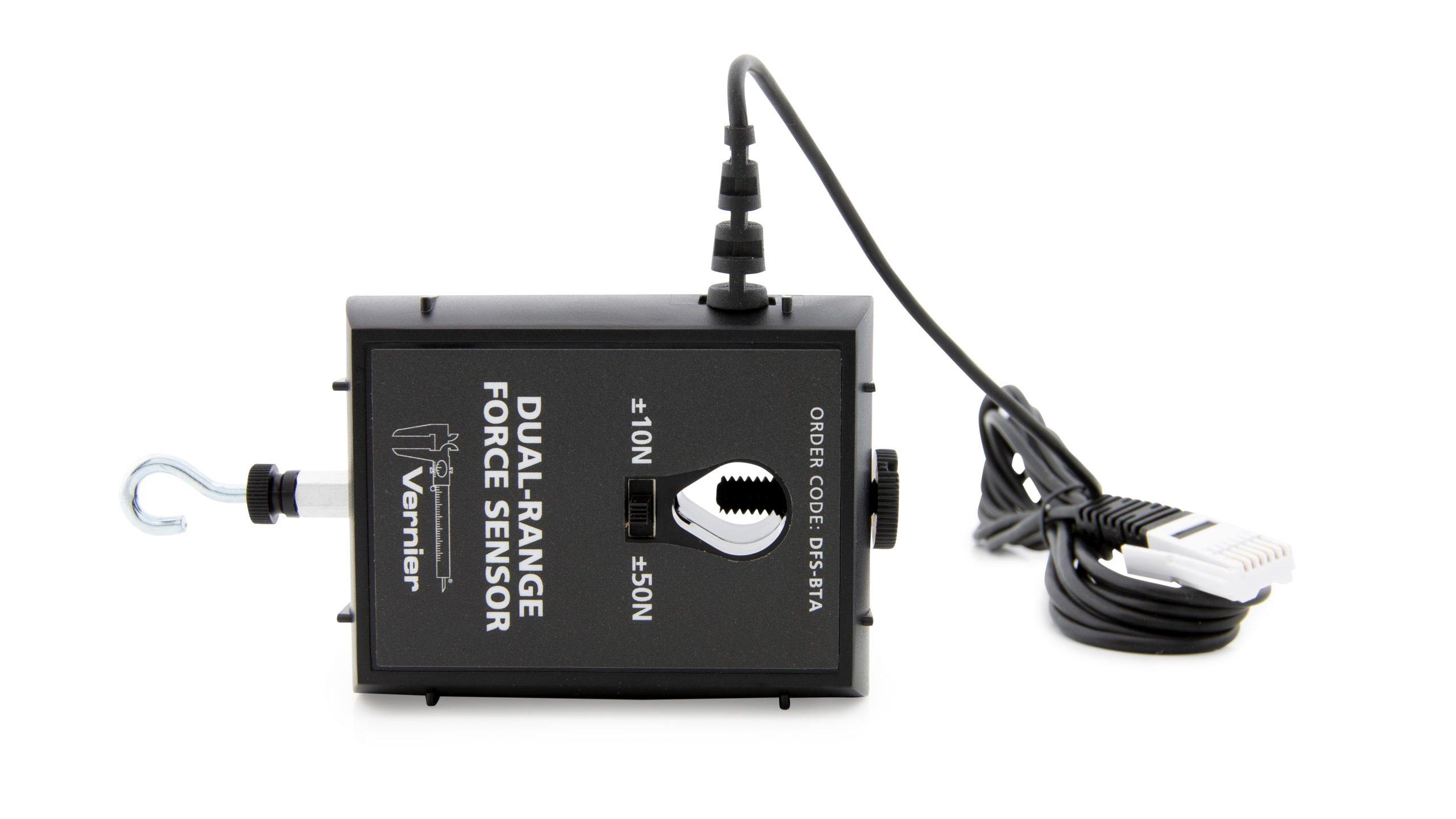
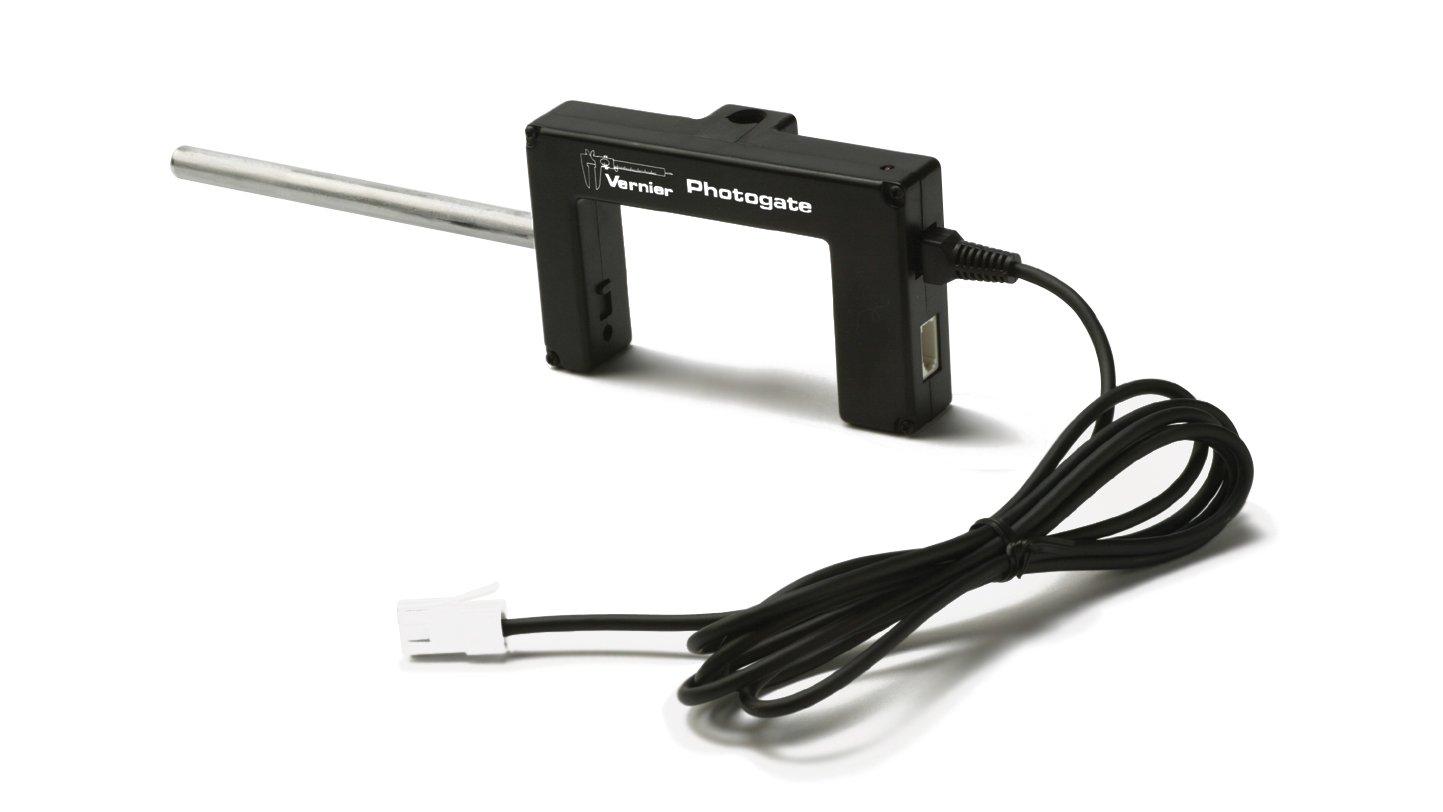
- Collect force, velocity, and radius data for a mass undergoing uniform circular motion.
- Analyze the force vs. velocity, force vs. mass, and force vs. radius graphs.
- Determine the relationship between force, mass, velocity, and radius for an object undergoing uniform circular motion.
- Use this relationship and Newton’s second law to determine an expression for centripetal acceleration.
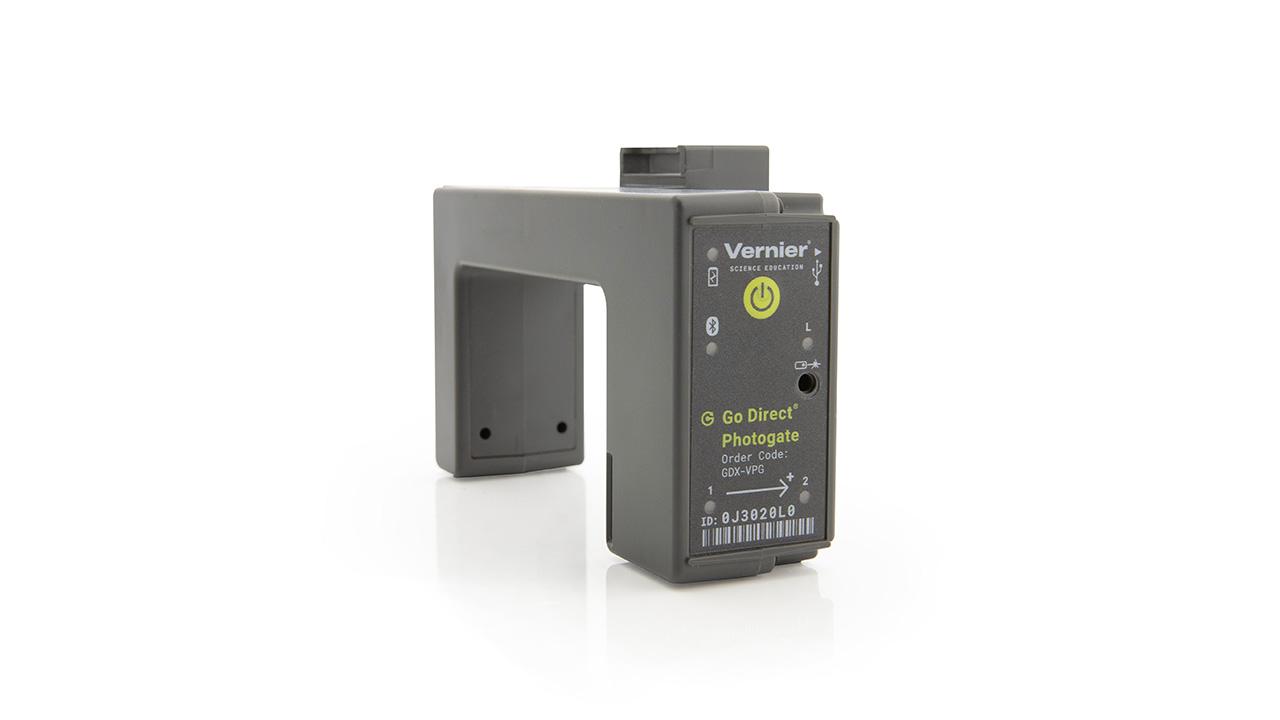
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #12 of Advanced Physics with Vernier — Mechanics. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.








