Wind Turbines: Effect of Load
Experiment #4 from Wind Energy Explorations
- Education Level
- Middle School
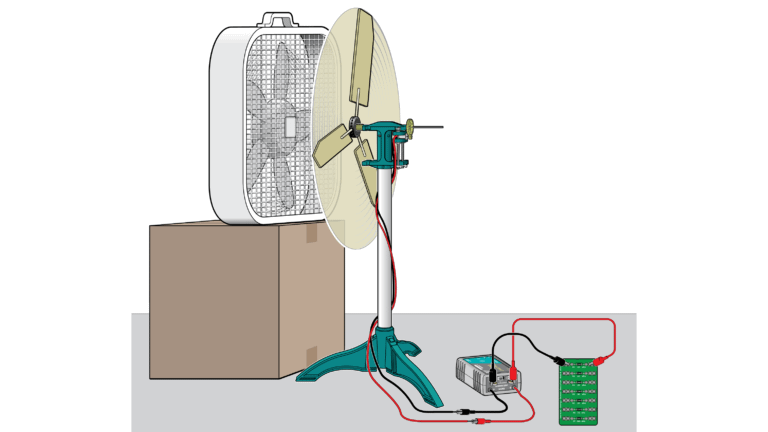
Introduction
A load is a device that uses electrical energy to accomplish its task. The simplest form of a load is a resistor. In most cases, resistors are used to adjust the amount of energy that reaches another load connected to the circuit by changing a voltage or diverting a current. Additional examples of loads include lights, fans, heaters, and more complicated devices such as televisions or computers. Any device that uses electricity can be considered a load.
In this experiment, you will measure the power output of a wind turbine and determine the optimal load. That is, you will determine the resistance for which the power output is greatest. You will then compare the optimal load to the internal resistance of the generator.
Objectives
- Determine how the power output of a wind turbine varies depending on the resistance (load) in the circuit.
- Compare internal resistance and optimal load.
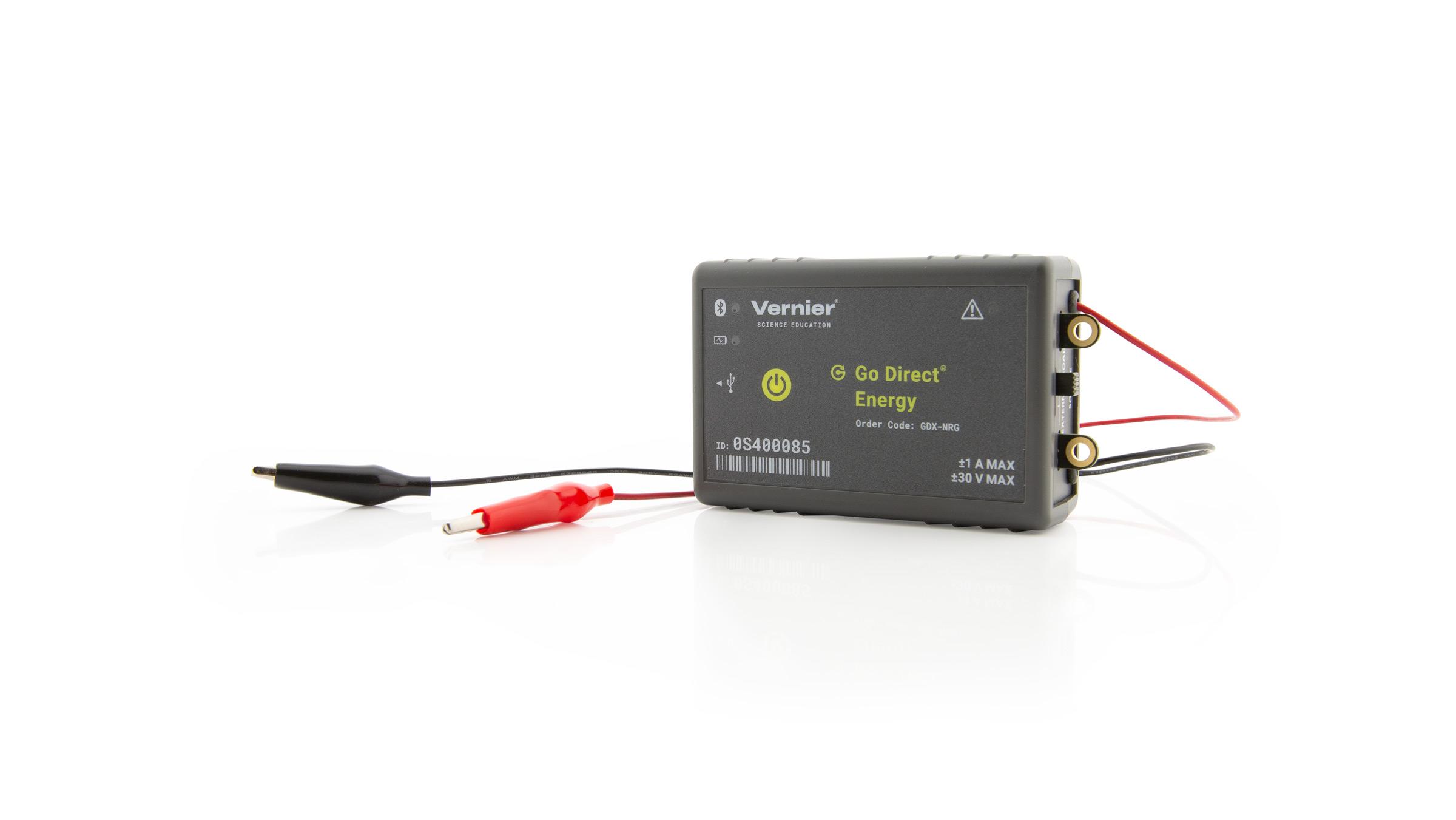
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #4 of Wind Energy Explorations. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.




