Introduction
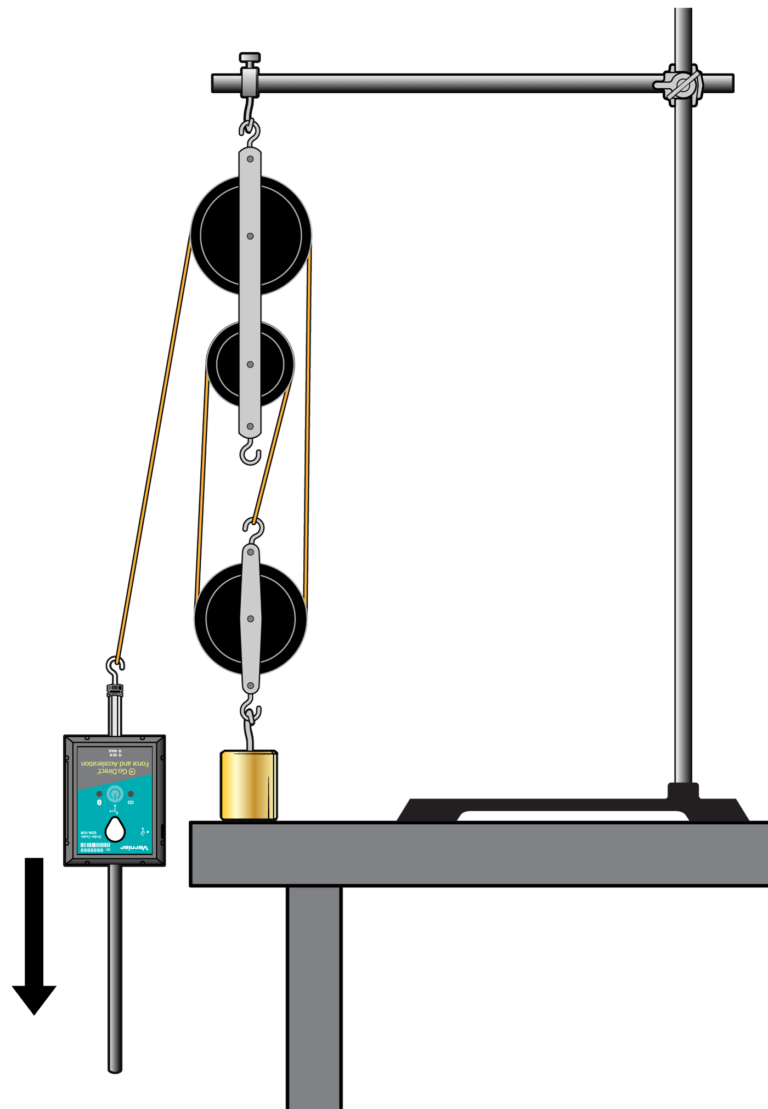
A pulley is a simple machine having a string that passes over a grooved wheel. A fixed pulley (see Figure 1) is attached to a solid support and changes the direction of force. The resistance force is the weight of the object being lifted. This force is applied to one end of the string that goes over a fixed pulley. The effort force is exerted on the other end of the string, in opposition to the resistance force. A movable pulley moves along the string with the resistance force, and the direction of the force is not changed. A pulley system may have a single pulley or a combination of pulleys. Pulley systems are used to make work easier.
Mechanical advantage is a value that tells the number of times a machine increases the applied force. In this experiment, you will use a Force Sensor to measure the effort force (in N) for three different pulley systems and then determine the mechanical advantage of each system.
Objectives
- Use a Force Sensor to measure force.
- Calculate actual mechanical advantage and ideal mechanical advantage.
- Determine efficiency.
- Make conclusions about pulley systems.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #10 of Exploring Physical Science. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.


