Introduction
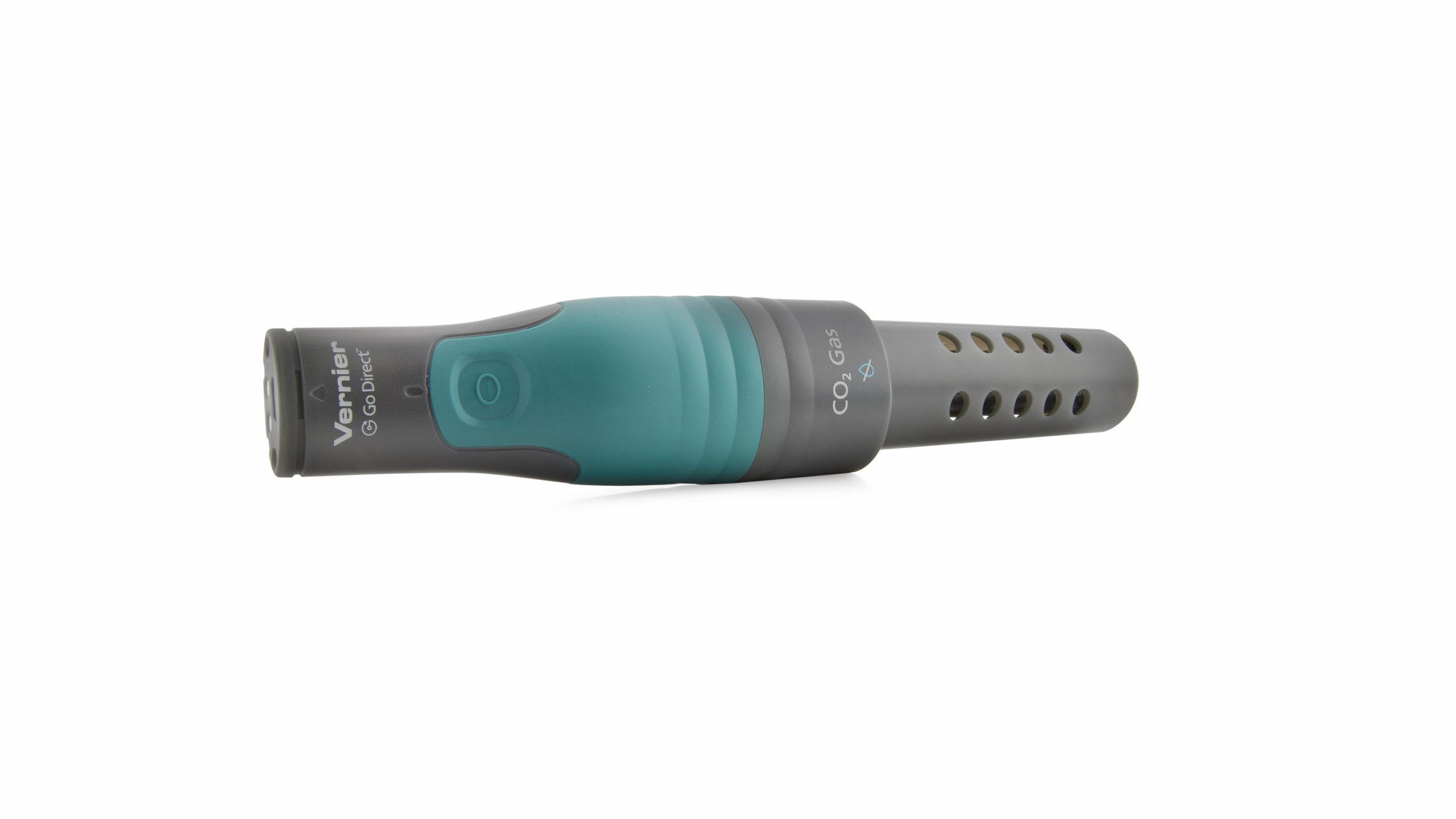
In this experiment, you will set up a plausible scenario for how this crime might have been committed. One possibility that you will study is filling the room with carbon dioxide gas, CO2, which would eventually cause suffocation.
Your job will be to simulate the time required filling the room to 40,000 ppm with CO2. You will also calculate the mass of dry ice, solid CO2, that would be required to fill the room.
Using a 3 L bottle to model Chad Barlson’s cabin, you will measure the rate at which carbon dioxide gas, CO2, might have been introduced into the cabin. From the rate data, you will extrapolate to determine how much dry ice would be required to fill the room with CO2.
Objectives
- Measure the rate of diffusion of CO2 gas in a model of the cabin.
- From the room dimensions, calculate the mass of CO2 needed to fill the room with 40,000 ppm CO2 gas.
- Determine how long it would take to fill the cabin with CO2 using your rate data.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Correlations
Teaching to an educational standard? This experiment supports the standards below.
- International Baccalaureate (IB) 2025/Chemistry
- Structure 1.5.4—The relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature and amount of an ideal gas is shown in the ideal gas equation PV = nRT and the combined gas law P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #8 of Forensic Chemistry Experiments. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.