Introduction to the Vernier Energy Sensor
Experiment #3 from Investigating Solar Energy
- Education Level
- Elementary School
Introduction
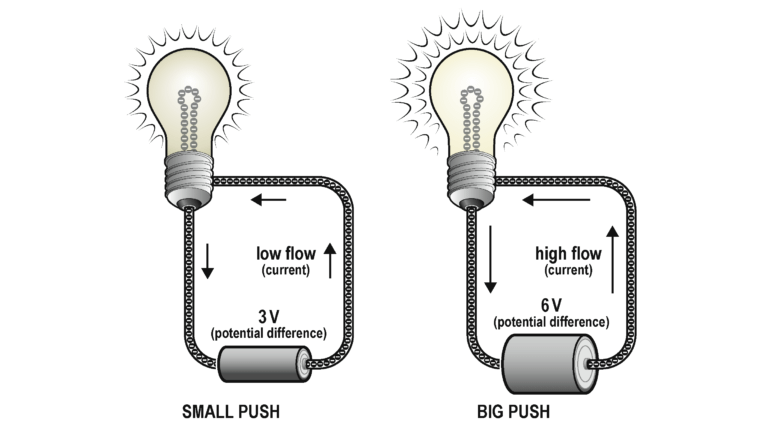
When sunlight hits a solar panel, the energy of the sun is transferred to the electrons that make up the solar panel. This causes the electrons to start moving through the wires connected to the panel. In this experiment, you will use a Vernier Energy Sensor to measure the electrons as they move. Three values are used to measure the movement of electrons: current, potential difference, and power.
Objectives
- Set up the data-collection equipment.
- Measure current, potential difference (voltage), and power output of a Solar Panel with a Vernier Energy Sensor.
- Use data-collection software to calculate mean (average) values.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #3 of Investigating Solar Energy. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.





