Freezing and Melting of Water
Experiment #2 from Chemistry with Vernier
- Education Level
- High School
- Subject
- Chemistry
Video Overview
Introduction
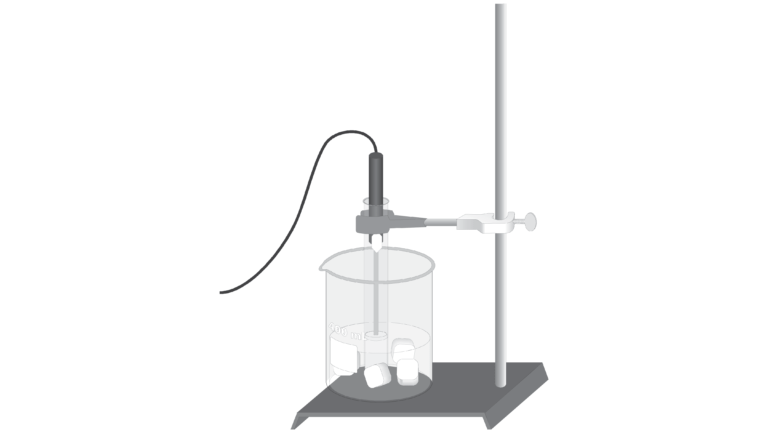
Freezing temperature, the temperature at which a substance turns from liquid to solid, and melting temperature, the temperature at which a substance turns from a solid to a liquid, are characteristic physical properties. In this experiment, the cooling and warming behavior of a familiar substance, water, will be investigated. By examining graphs of the data, the freezing and melting temperatures of water will be determined and compared.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Collect temperature data during the freezing and melting of water.
- Analyze graphs to determine the freezing and melting temperatures of water.
- Determine the relationship between the freezing and melting temperatures of water.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1
Correlations
Teaching to an educational standard? This experiment supports the standards below.
- International Baccalaureate (IB) 2025/Biology
- A1.1.1—Water as the medium for life
- A1.1.2—Hydrogen bonds as a consequence of the polar covalent bonds within water molecules
- A1.1.3—Cohesion of water molecules due to hydrogen bonding and consequences for organisms
- International Baccalaureate (IB) 2025/Chemistry
- Structure 1.1.3—The temperature, T, in Kelvin (K) is a measure of average kinetic energy Ek of particles
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #2 of Chemistry with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.


