An Investigation of Urea-Containing Cold Packs
Experiment #3 from Investigating Chemistry through Inquiry
- Subject
- Chemistry
Introduction
An instant cold pack usually consists of a rugged plastic bag with water and a soluble compound inside. The water is sealed in a fragile inner bag to keep it separated from the solid. When the cold pack is needed, it is squeezed to break open the inner container and bring the water and solid together. As the water and solid interact, heat is absorbed and temperature decreases.
Ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3, has been the solid most often used in instant cold packs. But, because it is much less hazardous, urea, (NH2)2CO, is replacing ammonium nitrate for this use. In this experiment, you will investigate the properties of urea and urea-containing cold packs.
Objectives
In the Preliminary Activity, you will gain experience using a Temperature Probe as you determine the temperature change as a sample of urea dissolves in water.
After completing the Preliminary Activity, you will first use reference sources to find out more about cold packs, urea, and heat before you choose and investigate a researchable question dealing with urea or urea-containing cold packs.
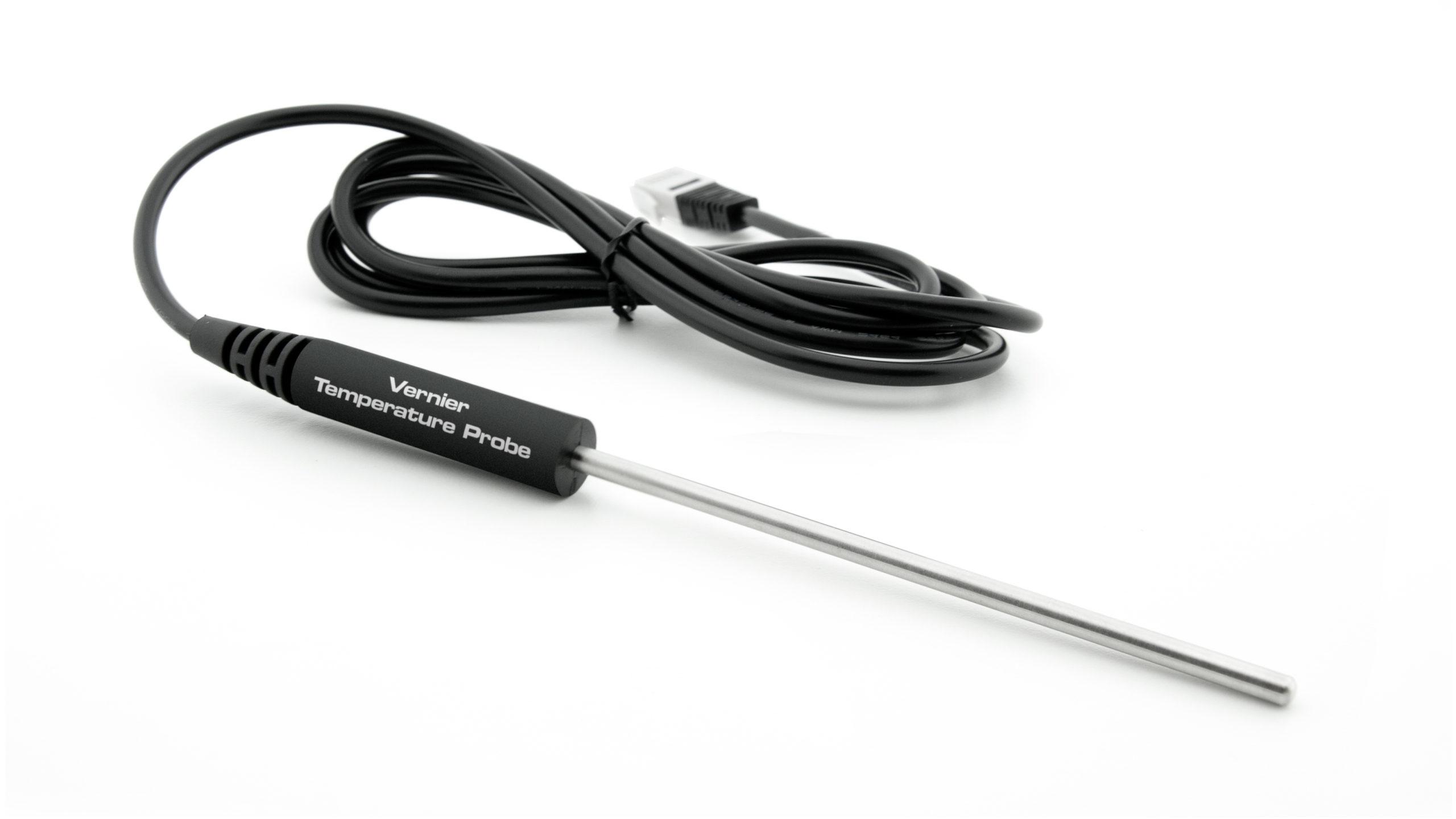
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #3 of Investigating Chemistry through Inquiry. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.


