Introduction
In this experiment, you will determine the molar volume of a gas by conducting a chemical reaction that produces a gas, as shown in the reaction equation below.
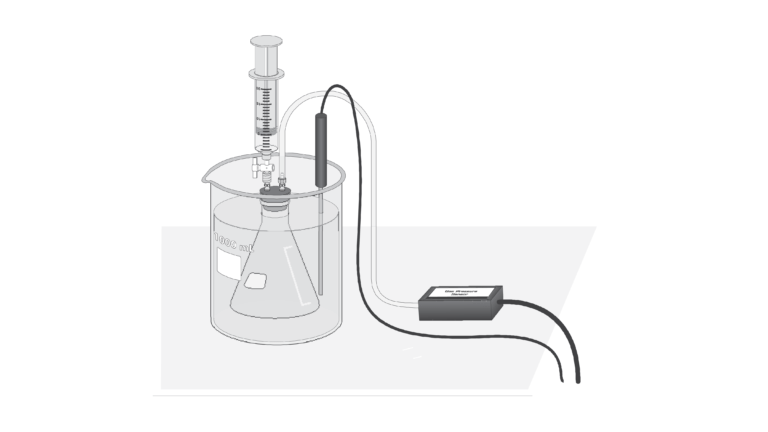
You will react a known mass of solid magnesium with an excess of hydrochloric acid, in a sealed vessel, and use the pressure change to calculate molar volume at STP.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Measure the gas production of a chemical reaction by a pressure change.
- Determine the molar volume of the gas produced in the reaction.
- Calculate the molar volume of a gas at STP.
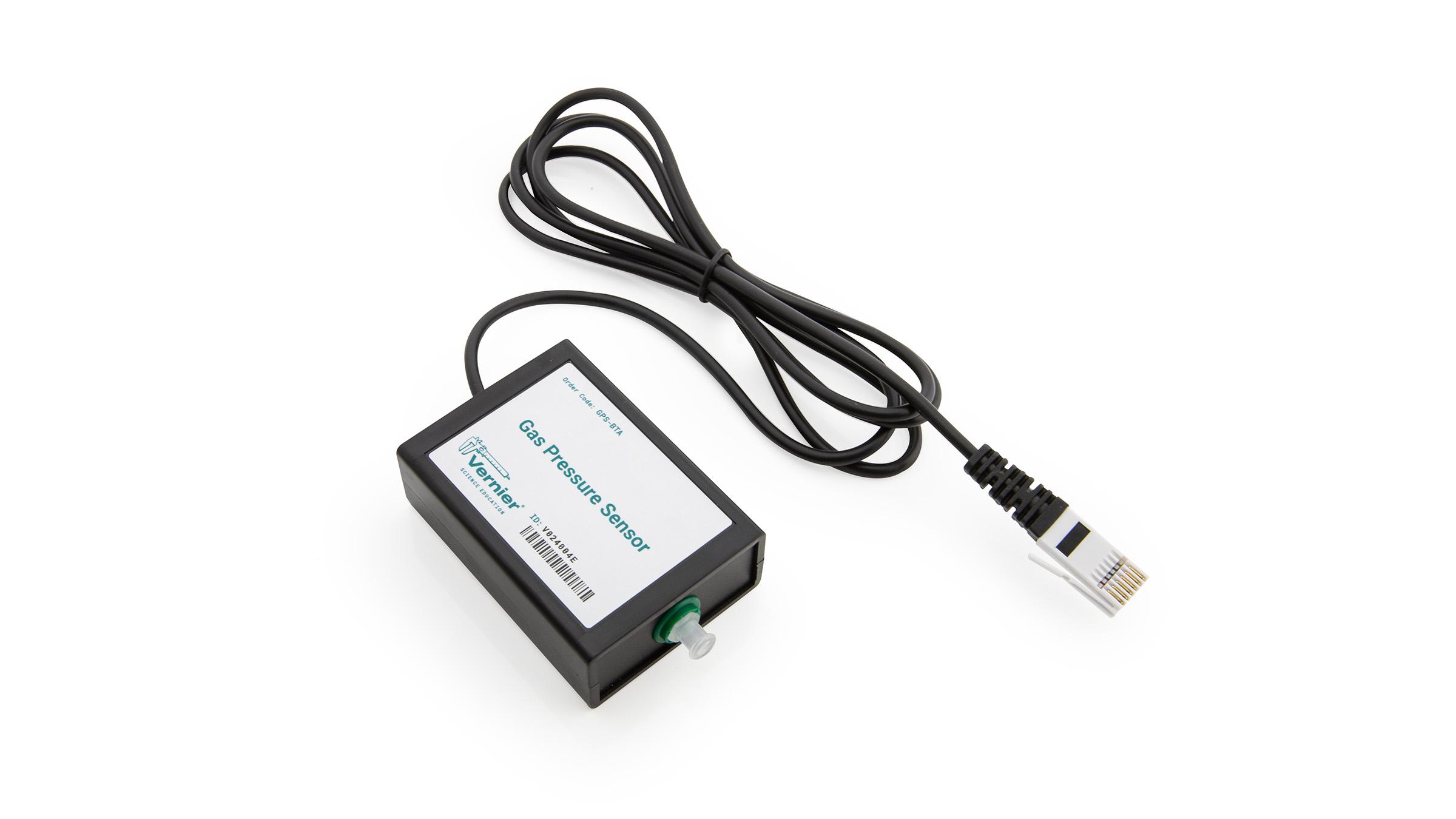
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Correlations
Teaching to an educational standard? This experiment supports the standards below.
- International Baccalaureate (IB) 2025/Chemistry
- Structure 1.5.3—The molar volume of an ideal gas is a constant at a specific temperature and pressure.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #5 of Advanced Chemistry with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.