Introduction
Water is transported in plants, from the roots to the leaves, following a decreasing water potential gradient. Transpiration, or loss of water from the leaves, helps to create a lower osmotic potential in the leaf. The resulting transpirational pull is responsible for the movement of water from the xylem to the mesophyll cells into the air spaces in the leaves. The rate of evaporation of water from the air spaces of the leaf to the outside air depends on the water potential gradient between the leaf and the outside air.
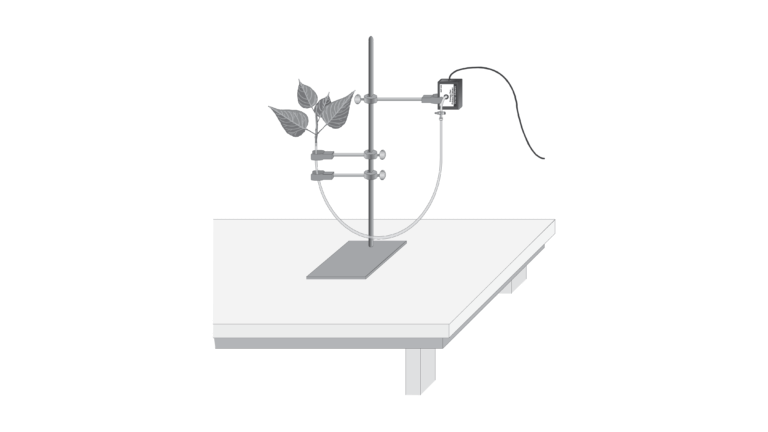
Various environmental factors, including those conditions which directly influence the opening and closing of the stomata, will affect a plant’s transpiration rate. This experiment will measure transpiration rates under different conditions of light, humidity, temperature, and air movement. The data will be collected by measuring pressure changes as the plant takes up water into the stem.
Objectives
In this experiment, you will
- Observe how transpiration relates to the overall process of water transport in plants.
- Use a Gas Pressure Sensor to measure the rate of transpiration.
- Determine the effect of light intensity, humidity, wind, and temperature on the rate of transpiration of a plant cutting.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Option 1

Option 2

Correlations
Teaching to an educational standard? This experiment supports the standards below.
- International Baccalaureate (IB) 2025/Biology
- B3.1.7—Adaptations for gas exchange in leaves
- B3.1.8—Distribution of tissues in a leaf
- B3.1.9—Transpiration as a consequence of gas exchange in a leaf
- B3.1.10—Stomatal density
- B3.2.7—Transport of water from roots to leaves during transpiration
- B3.2.8—Adaptations of xylem vessels for transport of water
- D2.3.4—Changes due to water movement in plant tissue bathed in hypotonic and those bathed in hypertonic solutions
- D2.3.6—Effects of water movement on cells with a cell wall
- D2.3.11—Water potential and water movements in plant tissue
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #10 of Biology with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.

