Shop
- Engineering
- Arduino
- Using Vernier Sensors with Arduino Guide
- Connecting Vernier Sensors to Arduino
Connecting Vernier Sensors to Arduino®
There are two ways to connect Vernier sensors to Arduino. You can plug any standard Vernier sensor with a BTA or BTD connector directly into a Vernier Arduino Interface Shield or you make your own wired connections with a breadboard and one or more Vernier Protoboard Adapters.
The method you choose will depend on the complexity of your project. Be sure to use an Arduino board that operates at 5 volts; standard Vernier sensors will not work on 3.3-volt Arduino boards at this time.
Connecting Vernier Sensors to Arduino Using Vernier Arduino Interface Shield
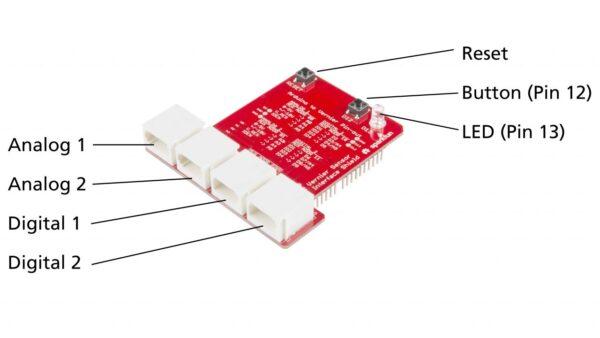

Connecting Vernier Sensors to Arduino Using a Breadboard
Another way to make the connection from the Arduino to Vernier sensors is to use our Analog Protoboard Adapter and Digital Protoboard Adapter.
These adapters were designed to plug into a breadboard using jumper wires to make connections from the breadboard to the Arduino pins. Choose the Analog Protoboard Adapter if you are using analog (BTA) sensors, the Digital Protoboard Adapter if you are using digital (BTD) sensors, or both if you will be using both types of sensors.
Our protoboard adapters have six pins. The pins are labeled on the adapters starting with the pin farthest from the tab on the socket. In order for Vernier library commands and sample sketches to work properly, be sure to make your connections between the breadboard and Arduino according to the pinouts listed below. Note these pin connections are identical to those used on the Vernier Arduino Interface Shield.

Analog Protoboard Adapters
- SIG2 (Vernier BTA pin 1) to Arduino pin A1 (+/-10V output used by just a few Vernier analog sensors)
- GND (Vernier BTA pin 2) to Arduino pin GND (ground)
- Vres (Vernier BTA pin 3) to Arduino pin A4 (resistance reference)
- ID (Vernier BTA pin 4) to Arduino pin A5 (not used by all sensors)
- 5V (Vernier BTA pin 5) to Arduino pin 5V (power)
- SIG1 (Vernier BTA pin 6) to Arduino pin A0 (0-5V output used by almost all Vernier sensors)
Wiring a Second Analog Protoboard Adapter
A second Analog Protoboard Adapter allows you to use two Vernier analog sensors at once with your Arduino.
- SIG2 (Vernier BTA pin 1) to Arduino pin A3 (+/-10V output used by just a few Vernier analog sensors)
- GND (Vernier BTA pin 2) to Arduino pin GND (ground)
- Vres (Vernier BTA pin 3) to Arduino pin A4 (resistance reference)
- ID (Vernier BTA pin 4) to Arduino pin A5 (not used by all sensors)
- 5V (Vernier BTA pin 5) to Arduino pin 5V (power)
- SIG1 (Vernier BTA pin 6) to Arduino pin A2 (0-5V output used by almost all Vernier sensors)
Digital Protoboard Adapters
- DIO0 (Vernier BTD pin 1) to Arduino pin 2 (function depends on sensor)
- DIO1 (Vernier BTD pin 2) to Arduino pin 3 (function depends on sensor)
- DIO2 (Vernier BTD pin 3) to Arduino pin 4 (function depends on sensor)
- 5V (Vernier BTD pin 4) to Arduino pin 5V (power)
- GND (Vernier BTD pin 5) to Arduino pin GND (ground)
- DIO3 (Vernier BTD pin 6) to Arduino pin 5 (function depends on sensor)
Wiring a Second Digital Protoboard Adapter
A second Digital Protoboard Adapter allows you to use two Vernier digital sensors at once or a digital sensor in conjunction with the Vernier Digital Control Unit (DCU) or the Vernier DCU by itself. Be aware that the VernierLib commands assume the sensor is plugged into the first adapter and the DCU is plugged into the second adapter.
- DIO0 (Vernier BTD pin 1) to Arduino pin 6 (function depends on sensor)
- DIO1 (Vernier BTD pin 2) to Arduino pin 7 (function depends on sensor)
- DIO2 (Vernier BTD pin 3) to Arduino pin 8(function depends on sensor)
- 5V (Vernier BTD pin 4) to Arduino pin 5V (power)
- GND (Vernier BTD pin 5) to Arduino pin GND (ground)
- DIO3 (Vernier BTD pin 6) to Arduino pin 9 (function depends on sensor)
Arduino® and

are trademarks of Arduino SA.
