Introduction
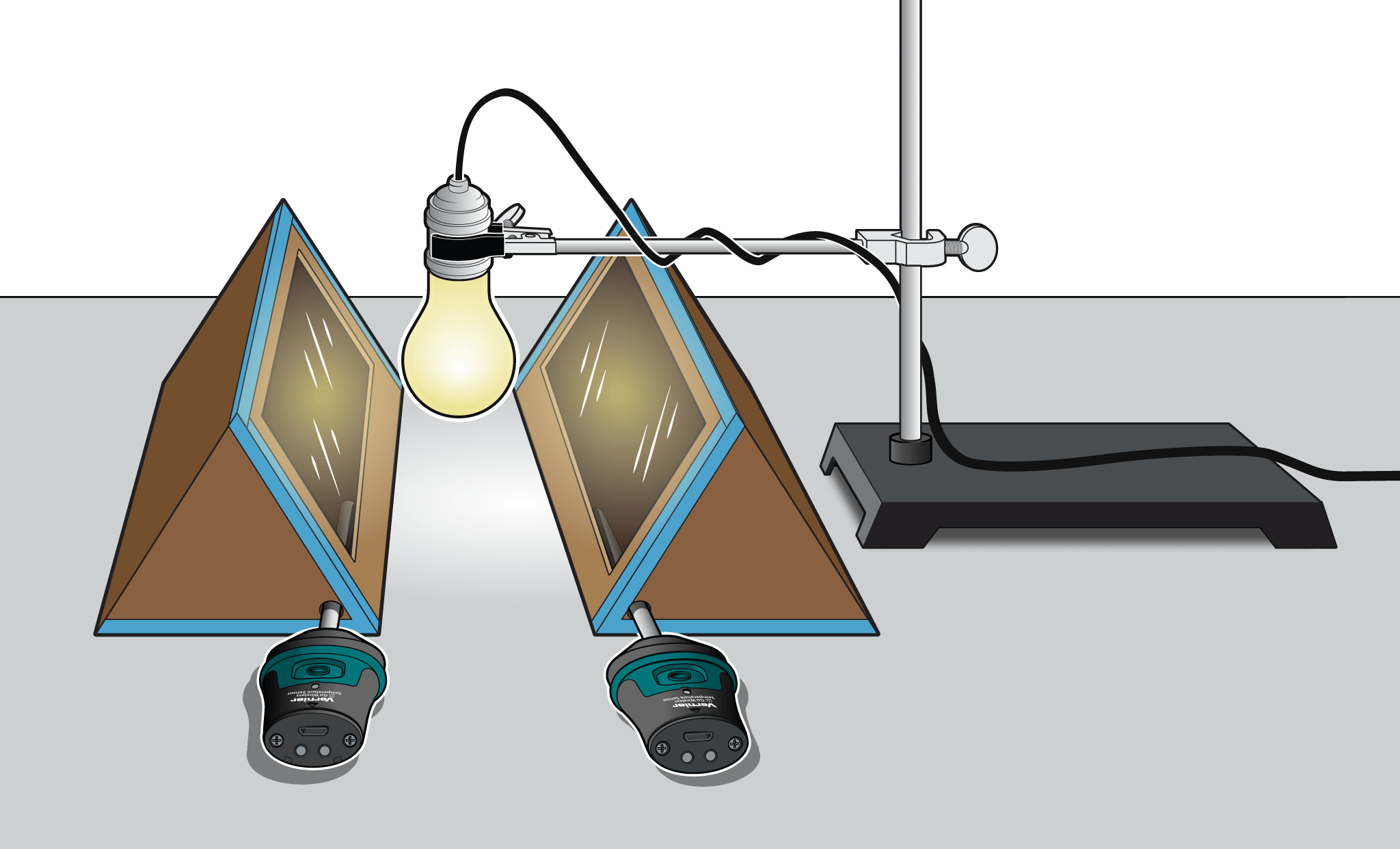
Alternative energy sources are energy sources other than the nonrenewable fossil fuels—coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Solar energy, or energy from the sun, is one energy source alternative. A passive solar heating system uses no pumps, fans, or mechanical devices. Insulation and heat storage are important factors in such a system. Heat can be stored using thermal masses, also called heat sinks. Thermal masses can keep a home from heating or cooling too fast.
In this experiment, you will examine the effectiveness of a heat sink. Two model homes, one with a heat sink and one without, will be heated by a light bulb. Two temperature probes will monitor their temperatures throughout a simulated day and night. You will then use what you learn to design and build a model solar home.
Objectives
- Use temperature probes to measure temperature.
- Find the relationship between heat sink and the ability of a solar home to retain heat.
- Design, build, and test a model solar home.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
Ready to Experiment?
Ask an Expert
Get answers to your questions about how to teach this experiment with our support team.
- Call toll-free: 888-837-6437
- Chat with Us
- Email support@vernier.com
Purchase the Lab Book
This experiment is #31 of Earth Science with Vernier. The experiment in the book includes student instructions as well as instructor information for set up, helpful hints, and sample graphs and data.